Penn State Turns to 3D Printing, Online Learning to Teach Students About the Brain
A Pennsylvania State
University research project is exploring the use of 3D printing
and interactive technology to teach middle school students about the
human
brain.
Researchers in the Brain3M project, funded by the Penn State Social Science Research Institute,
have come
up with a tailored online learning platform that allows students to go
through
a series of virtual 3D structure models and descriptions of the brain
along
with photos and diagrams that illustrate the complex concepts
concerning how
the human brain works.
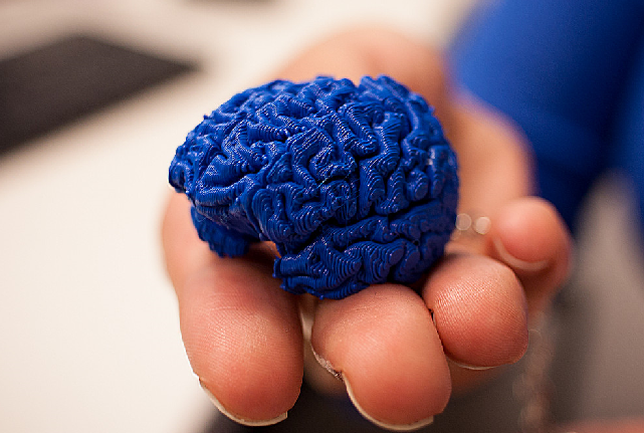
Students in the Brain3M program each receive their own 3D printed model of the human brain so they can closely examine it themselves.
Likewise, students in the
program each receive their own 3D printed model of the human brain so
they can
closely examine it themselves.
"The students can click on
any parts of the brain in any order they want, so we're really letting
them
make their own decisions about their learning," said Jennifer Legault,
a
graduate student at Penn State's College of Information Sciences and Technology. "The kids seemed to like that they could take control of
their own
learning experience and go at their own pace."
In order to test the
effectiveness of the Brain 3M project (which stands for mobile devices,
magnetic resonance imaging and 3D models), researchers took pilot
programs to
the Young Scholars of Central Pennsylvania Charter School and the
Science-U summer camp that is held annually on the Penn State campus for middle
school
students.
Participants were taught two
different lessons involving brain science, one with the interactive
Brain3M
website and the other with a PowerPoint presentation.
Although the sample sizes of
the groups were too small to yet draw any substantial conclusions,
researchers
indicated that students were more excited and engaged by the Brain3M
platform.
All students received the 3D models of the brain on keychains as
souvenirs.
"More than 80 percent of the
participants said they would want to use this website again to learn
about the
brain," Legault said.
About the Author
Michael Hart is a Los Angeles-based freelance writer and the former executive editor of THE Journal.