'Good Jobs' Still Exist; Most Require Post-High School Education
- By Dian Schaffhauser
- 08/03/17
Good jobs — those that pay at least $35,000 a year — don't necessarily require a bachelor's degree. These good jobs have a median salary of $55,000. And 30 million of them exist in this country, compared to 36 million "good jobs" for workers with four-year college degrees. The share of good jobs held by those without a BA has shrunken from 60 percent in 1991 to 45 percent today. Those are the singular findings of a research project undertaken by the Georgetown University Center on Education and the Workforce and supported by JPMorgan Chase & Co to understand the impact of economic change wrought by the Great Recession.
People without a bachelor's degree make up two-thirds (64 percent) of all workers. According to the authors of "Good Jobs that Pay without a BA," many of those workers believe they can no longer find good jobs. For example, while manufacturing has the reputation of having virtually disappeared in the United States, taking along its union-bolstered wages, it's not entirely true, suggested Anthony Carnevale, director of the center and lead author of the report. While manufacturing accounted for nearly all of the good jobs that non-bachelor's workers have lost since 1991, that segment "still provides the largest number of good jobs," he noted.
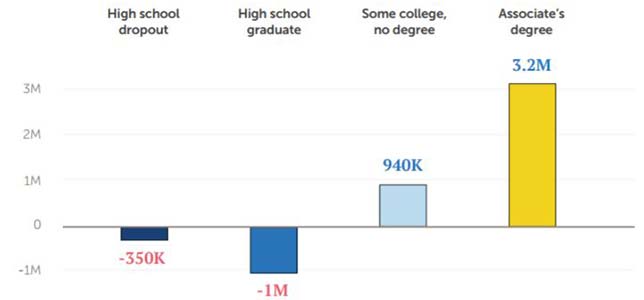
The increase in good jobs for associate's degree holders offset the losses experienced by those with high school diplomas. Source: Georgetown University Center on Education and the Workforce analysis of Current Population Survey Annual Social and Economic Supplement (March), 1992-2016.
The research project found that 4 million good jobs have materialized in "skilled services," segments, such as financial services and health services, offsetting the estimated 2.8 million good jobs lost in manufacturing.
However, the report emphasized, new good jobs do require at least some post-secondary education and training. Those workers with only high school diplomas still have the largest share of good jobs (11.6 million), but that proportion is shrinking. Workers with some college have 9.3 million good jobs; those who have earned their associate's degrees have 7.6 million good jobs; and high school dropouts hold just 1.7 million good jobs.
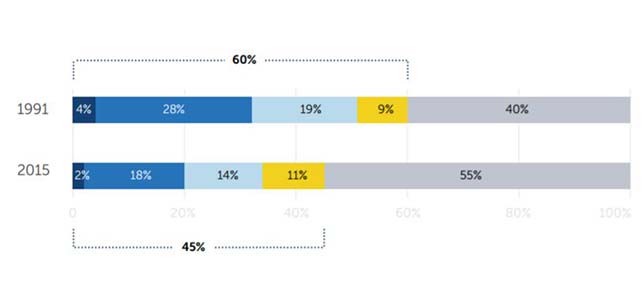
Between 1991 and 2015 the number of good jobs going to workers lacking a four-year degree fell by 15 percentage points. Source: Georgetown University Center on Education and the Workforce analysis of Current Population Survey Annual Social and Economic Supplement (March), 1992-2016.
Among all of those workers, men dominate, grabbing seven in 10 good jobs. Whites hold more good jobs than Latinos, while blacks have the smallest share. The three largest state economies in the country — California, Texas and Florida — have the largest number of good jobs for these workers, but good jobs make up a larger share of all jobs in three other states: Wyoming, New Jersey and Maryland.
This fall the center will continue releasing research related to this initiative on its "Good Jobs Project" website. The site will provide data by state, offer a "good jobs index" to allow users to determine the level of economic opportunity for workers without four-year degrees across the country; and let people drill down on good jobs by industry and occupation.
The full report is openly available on the Good Jobs Data website here.
About the Author
Dian Schaffhauser is a former senior contributing editor for 1105 Media's education publications THE Journal, Campus Technology and Spaces4Learning.