Security Professionals Express Cautious Optimism About AI
A new report on the state of AI and security indicates that security pros are cautiously optimistic about AI's potential to enhance threat detection and response.
The State of AI and Security Survey Report was published by the Cloud Security Alliance (CSA), a not-for-profit organization that promotes best practices for ensuring cybersecurity in cloud computing and IT technologies. The study was commissioned by Google Cloud and conducted online by the CSA in November 2023, receiving 2,486 responses from IT and security professionals from organizations in various industries around the world, including education.
The report outlines the current state of AI in cybersecurity, highlighting key findings and patterns that emerged from the survey. Here are some of the key takeaways from the report:
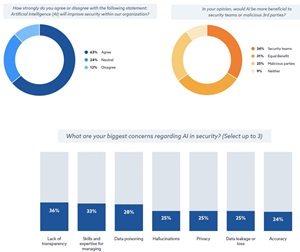
- A majority of security professionals (63%) believe in AI's potential to enhance security measures, especially in improving threat detection and response capabilities.
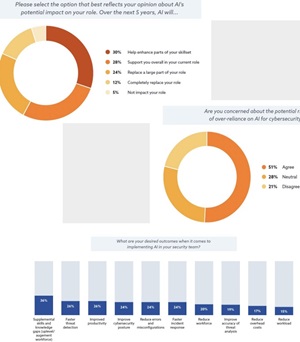
- Only a small fraction (12%) of security professionals believe AI will completely replace their role. The majority believe it will help enhance their skill set (30%), support their role generally (28%), or replace large parts of their role (24%), freeing them up for other tasks.
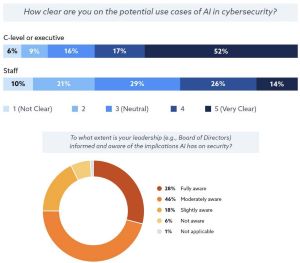
- C-suite executives demonstrate a notably higher (52%) self-reported familiarity with AI technologies than their staff (11%).
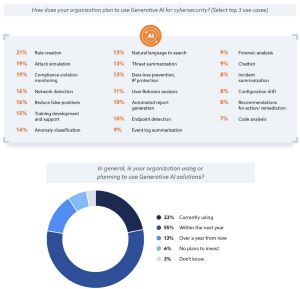
- 2024 is set to be a revolutionary year for AI implementation in the security sector. Over half of organizations (55%) are planning to implement generative AI solutions this year.
Here are the data points backing up those findings:
Cautious Optimism About AI Among Security Professionals
 [Click on image for larger view.](source: CSA).
[Click on image for larger view.](source: CSA).
- Cautious Optimism: 63% of security professionals see AI as a boon for enhancing threat detection and response, expressing cautious optimism about its potential.
- Dual Nature Awareness: There's a split view on AI's benefits — 34% believe it favors security teams, while 31% see equal advantages for attackers and defenders. A notable 25% worry AI might favor malicious actors more.
- Top Concerns: Major apprehensions include data quality issues (38%), potentially leading to bias, opacity of AI systems, and gaps in skills/expertise needed to manage complex AI systems.
- Call for Strategy Evolution: Acknowledgment of AI's misuse potential and the necessity for evolving security strategies, rigorous data handling, and enhancing AI system transparency.
- Security Framework Need: Highlighting the importance of developing comprehensive frameworks to secure AI technologies in cybersecurity.
AI Will Empower, not Replace, Security Professionals
 [Click on image for larger view.](source: CSA).
[Click on image for larger view.](source: CSA).
-
AI as an Empowerment Tool: Majority view AI as enhancing their skills (30%), supporting their roles (28%), or automating large parts of their tasks (24%), with only 12% fearing total replacement.
- Role Enhancement through AI: Security professionals see AI as enhancing their skills (30%), supporting their roles (28%), or automating parts of their work (24%), thus freeing them for other tasks.
- Discrepancy in Challenges vs. AI Goals: Despite emphasizing AI for skills enhancement, immediate challenges like operational toil and threat detection are ranked higher than talent issues.
- Concerns Over AI Reliance: 50% of respondents worry about over-reliance on AI, stressing the importance of balancing AI-driven and human-driven security approaches.
C-Suite Executives Have Different AI Perspectives from Their Staff
 [Click on image for larger view.](source: CSA).
[Click on image for larger view.](source: CSA).
- Discrepancy in AI Familiarity: 52% of C-suite executives report being very familiar with AI, versus 11% of staff.
- Understanding of AI Use Cases: 51% of C-levels have a clear understanding, compared to 14% of staff, suggesting a knowledge gap or overestimation of familiarity by executives.
- Leadership Awareness: 74% believe their leadership is informed about AI's implications on security.
- AI Adoption Push: 82% note executive leadership and boards are advocating for AI adoption, indicating top-down pressure.
- Need for Enhanced Communication: Highlights the importance of improved education and collaborative approaches to AI implementation in cybersecurity.
2024 Is the Year for AI Implementation — Get Ready for the Revolution
 [Click on image for larger view.](source: CSA).
[Click on image for larger view.](source: CSA).
- Over half (55%) of organizations are planning to implement gen AI solutions in the next year
- A diverse range of use cases are being explored with the top use cases: rule creation (21%), attack simulation (19%), and compliance violation detection (19%)
- Biggest hurdle to AI implementation is the skills gap and staff shortage, as reported by 33% of respondents.
"The advent of artificial intelligence (AI) in cybersecurity marks a transformative era in the realm of digital defense. AI has the potential to be a vital ally for bolstering security defenses, identifying emerging threats, and facilitating swift responses. However, the journey towards integrating AI into security workflows is fraught with obstacles, including the need to mitigate dual-use concerns, bridge skill gaps, and encourage appropriate reliance on automated systems," the report said.
About the Author
David Ramel is an editor and writer at Converge 360.