
Modest investments in the Internet of Things can have a significant impact on students' journey through college. Here's how one institution implemented IoT tech to provide extra student supports in key areas.

Three researchers argue in a recent article in the IEEE magazine that it's time to create an engineering discipline in more colleges and universities as well as vocational schools focused on the Internet of Things and cyber-physical systems.

Microsoft is the latest company to join a program at Carnegie Mellon University to experiment with "edge" computing, the idea of bringing computing and storage resources closer to the user to reduce latency and data traffic. The university's Open Edge Computing Initiative is running a set of projects to help researchers and industry understand the benefits and limitations of this technological approach.

Virginia's Liberty University has updated its stadium network infrastructure as part of an overall remodel undertaken as part of its decision to move its football team into a new NCAA division for the start of the 2019 season.
Talari Networks announced a new offering targeting the growing software-defined wide-area-network space, highlighting connectivity to multiple cloud services.

The ninth release of the OpenDaylight software-defined networking and network functions virtualization platform is out, adding new functionality and marking adoption gains.

A new study found that organizations across sectors, including education, are hard put to keep pace with new developments in the networking industry.

In response to greater faculty and student demand for faster internet speeds, Valdosta State University has expanded its bandwidth capacity from 2 gigabits per second to 5.
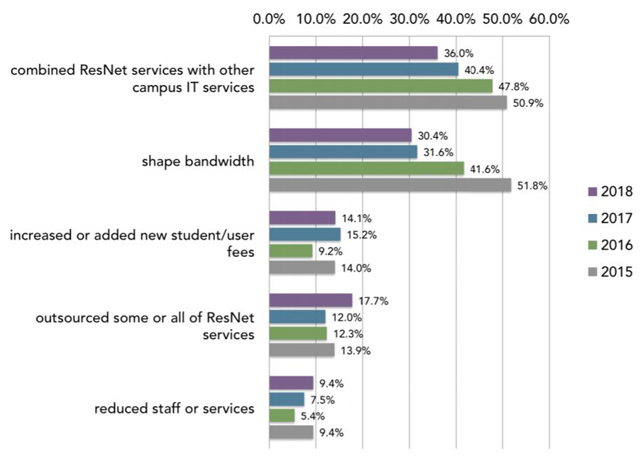
A recent survey among IT, housing and business people at colleges and universities found that the number of schools with a strategic plan incorporating the ResNet has fallen from 62 percent in 2017 to 52 percent this year.
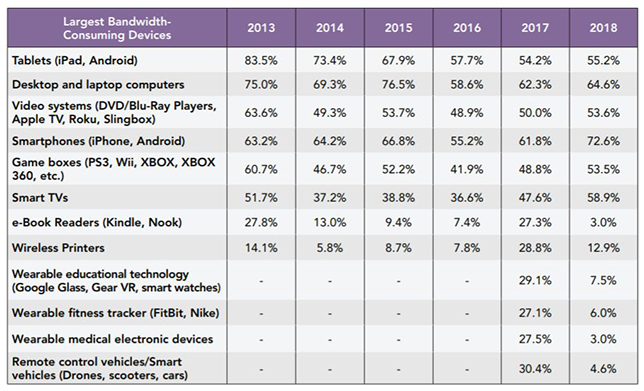
For the first time, smartphones top the list for having the greatest potential impact on bandwidth consumption on campus, surpassing desktop computers and laptops. In a survey on residential networks ("ResNets"), respondents consisting of IT, housing and business people at colleges and universities were asked to rate a list of devices based on the impact each could have on bandwidth consumption for the ResNet in coming years. iPhones and Androids were rated as having the most severe impact among 73 percent of survey participants, an 11 percentage point jump over 2017.