Next-Geners and Web 2.0
INCOMING FRESHMEN always come to campus with technology skills and expectations based previous experiences. More and more, they judge their new technology home-- your campus IT infrastructure and instructional applications of technology-- by the Web 2.0 and social software they've been using every day (in many cases, for their entire lives!).Herewith, an inside look at high school student use of Web 2.0 tools, from Project Tomorrow's Speak Up 2008 national survey of more than 335,000 K-12 students, teachers, parents,and administrators-- a clue to the expectations higher ed technologists and educators will be met with,in the coming freshman classes. According to Project Tomorrow CEO Julie Evans, "It is essential that our higher education leaders think beyond the current Web 2.0 applications and anticipate how the next generation will be using such tools to facilitate learning. Paying attention to how K-12 students are currently leveraging such tools for learning gives a unique perspective into the future."
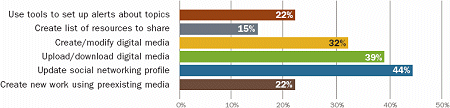
Web 2.0 Tools: Student Use for Creation (Grades 9-12)
High school students are using Web 2.0 tools to create and modify digital media, demonstrating knowledge,showing skill proficiency, and exercising self-expression.
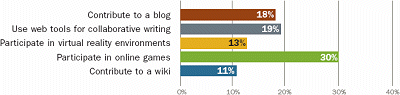
Web 2.0 Tools: Student Use for Collaboration and Contribution (Grades 9-12)
High school students are communicating and participating productively in online and virtual spaces.
Evans presented findings from the Speak Up 2008 study at her organization's annual National Congressional Briefing in Washington, DC, on March 24, 2009. Speak Up 2008 data used with permission from Project Tomorrow, a nonprofit organization focused on empowering students to have a greater voice in their education.