Arizona State U Launches Open, Adaptive Lessons on Space Exploration
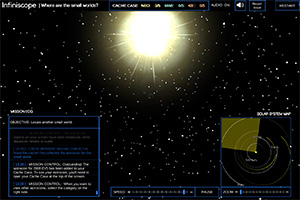
Infiniscope's "Where Are the Small Worlds?" module
Arizona State University has created a free series of digital lessons, simulations and virtual field trips designed to teach science through space exploration. Infiniscope uses content from NASA and adaptive learning technology from Smart Sparrow to engage students with a hands-on, interactive experience. The series is supported by a $10.18 million grant from NASA's Science Mission Directorate Education Community.
"Infiniscope makes the vastness of space and space exploration inviting, accessible and interactive for educators and learners of all ages," said Ariel Anbar, deputy principal investigator and director of ASU's Center for Education Through eXploration (ETX), in a statement. "The aim is to help learners become problem-solvers capable of exploring the unknown, rather than just mastering what is already known. Learning science should be approached as a process and as a universe of questions rather than as a dusty collection of facts."
The "Where Are the Small Worlds?" module, for example, asks participants to search a simulated solar system for asteroids and other objects. Learners "collect data on small worlds, observe the motion of different worlds to determine their location, and launch probes to discover 'astrocaches' hidden throughout the solar system," according to a press release. Adaptive technology provides feedback as learners are guided along individual pathways.
Infiniscope is part of the Inspark Science Network, an initiative launched in 2015 by Smart Sparrow and ASU's ETX with support from the Bill & Melinda Gates Foundation, which provides a community and platform for sharing digital courseware in science.
The first module of the series is available free to educators, administrators and learners on the Infiniscope site. ASU and Smart Sparrow say they will "continue to develop personalized and adaptive learning experiences and virtual field trips centered on astrobiology and 'small bodies' such as asteroids and Saturn's moon Enceladus."
About the Author
Rhea Kelly is editor in chief for Campus Technology, THE Journal, and Spaces4Learning. She can be reached at [email protected].