Human Factor Moves to No. 1 Cloud Threat in Cloud Security Alliance Report
The top cybersecurity threat in the cloud has changed from a couple years ago, according to a new report from the Cloud Security Alliance (CSA), which provided handy mitigation strategies and suggested AI can help (or hurt).
CSA recently published its Top Threats to Cloud Computing 2024 with data that is most interesting when compared to a similar 2022 report.
Comparing the two shows a familiar culprit has attained top-threat status: people. Specifically, in 2024 Misconfiguration & Inadequate Change Control has overtaken Identity & Access Management (IAM).
 [Click on image for larger view.] Top Threats Compared (source: CSA).
[Click on image for larger view.] Top Threats Compared (source: CSA).
"Traditional cloud security issues often associated with cloud service providers are continuing to decrease in importance," a spokesperson told Virtualization & Cloud Review. "These findings continue the trajectory first seen in the 2022 report, along with the fact that threats such the persistent nature of misconfigurations, Identity and Access Management (IAM) weaknesses, insecure application programming interfaces (APIs), and the lack of a comprehensive security strategy continue to rank high, highlighting their ongoing critical nature."
A Problem That Persists
This finding is nothing new, as a Thales report recently reached the same conclusion, along with several other similar studies (see "Cloud Security: Despite All the Tech, It's Still a People Problem").
"Human action can compromise security," said Thales in a cloud security report last month, the fourth in a series from the global technology company. "Fueling this concern is the high number of cloud data breaches, with 44 percent of respondents reporting such an incident. 14 percent reported a breach in the past 12 months. Human error, issues with vulnerability and configuration management, and failures to use Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA) are all cited as leading contributors."
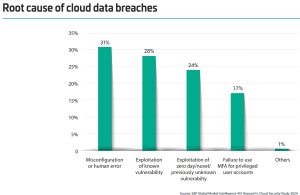 [Click on image for larger view.] Causes of Breaches (source: Thales).
[Click on image for larger view.] Causes of Breaches (source: Thales).
Yet other reports from earlier in the year sported similar themes (see Misconfigurations Continue to Plague Cloud Security, New Reports Say").
At that time, a CSA chart showed security misconfigurations as the No. 2 contributor to outages, below cloud provider issues.
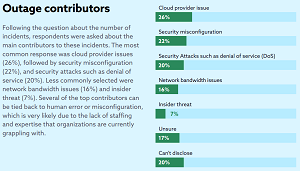 [Click on image for larger view.] "Several of the top contributors can
be tied back to human error or misconfiguration" (source: CSA).
[Click on image for larger view.] "Several of the top contributors can
be tied back to human error or misconfiguration" (source: CSA).
This has been an ongoing, high-profile problem for years, and despite all the publicity and mitigation advice it shows no signs of being lessening.
CSA said configuration management has been a cornerstone of organizational capability maturity for decades, but the transition to cloud computing compounded the challenges, so adopting more robust cloud-specific configurations is crucial. Misconfigurations can have wide-reaching impacts across an organization in view of a cloud's persistent network access and infinite capacity, the group said.
Michael Roza, co-chair of the CSA's Top Threats Working Group and one of the paper's lead authors, said: "It's tempting to think that the reason the same issues have remained in the top spots since the report was last issued stems from a lack of progress in securing these features. The larger picture, however, speaks to the importance placed on these vulnerabilities by organizations and the degrees to which they are working to build ever more secure and resilient cloud environments."
Here's what CSA had to say about the next three top threats of 2024:
- Identity and Access Management (IAM): Previously in the first spot, IAM now takes the second position. Challenges such as replay attacks, impersonation, and excessive permissions persist in cloud environments, similar to on-premise setups. However, the shift towards using self-signed certificates and poor cryptographic management raises significant security concerns. The focus on implementing Zero Trust architecture and software-defined perimeters (SDP) reflects these issues' prominence in our survey respondents' priorities.
- Insecure Interfaces and APIs: Moving to third from second, adopting microservices highlights the critical importance of securing interfaces and APIs. Despite their pivotal role in cloud services, including SaaS and PaaS offerings, substantial challenges remain in securing these elements due to coder inefficiencies and the always-on nature of the cloud.
- Inadequate Cloud Security Strategy: Remaining at the fourth position, this area continues to pose a question: Why do significant challenges in planning and architecting security solutions persist? Cloud computing has transcended its novelty status, necessitating a clearly defined and executed architectural strategy.
Future Outlook
Here is what the organization predicts for the future:
- Increased Attack Sophistication: Attackers will continue to develop more sophisticated techniques, including AI, to exploit vulnerabilities in cloud environments. These new techniques will necessitate a proactive security posture with continuous monitoring and threat-hunting capabilities.
- Supply Chain Risk: The growing complexity of cloud ecosystems will increase the attack surface for supply chain vulnerabilities. Organizations will need to extend security measures to their vendors and partners.
- Evolving Regulatory Landscape: Regulatory bodies will likely implement stricter data privacy and security regulations, requiring organizations to adapt their cloud security practices.
- The Rise of Ransomware-as-a-Service (RaaS): RaaS will make it easier for unskilled actors to launch sophisticated ransomware attacks against cloud environments. Organizations will need robust data backup and recovery solutions alongside strong access controls.
Mitigation Advice
And here is CSA's advice for mitigating the top threats:
- Integrating AI Throughout the SDLC (Software Development Life Cycle): Leveraging AI for tasks like code reviews and automated vulnerability scanning early in development will help identify and address security issues before the code reaches production.
- Utilizing AI-powered Offensive Security Tools: These tools simulate attacker behavior to discover vulnerabilities in cloud configurations, IAM protocols, and APIs. This proactive approach helps organizations stay ahead of potential threats.
- Cloud-native Security Tools: Organizations will increasingly adopt cloud-native security tools designed specifically for cloud environments. These tools offer better visibility and control than traditional security solutions.
- Zero Trust Security Model: The Zero Trust model emphasizes continuous verification and least privilege access and has become the standard for cloud security.
- Automation and Orchestration: Automating security processes and workflows will be essential for managing the complexity of cloud security at scale.
The not-for-profit CSA says it's dedicated to defining and raising awareness of best practices to help ensure a secure cloud computing environment. This latest report was based on two stages of research, both using surveys. In the first stage the group created a short list of cloud security issues through in-person surveys of group members, followed up by second-stage polling of more than 500 industry experts on a short-list of 28 security issues in the cloud industry to compile the final report.
The full report is available on the CSA site here.