Cloud Security Alliance: Best Practices for Securing AI Systems
The Cloud Security Alliance (CSA), a not-for-profit organization whose mission statement is defining and raising awareness of best practices to help ensure a secure cloud computing environment, has released a new report offering guidance on securing systems that leverage large language models (LLMs) to address business challenges.
Aimed at system engineers and architects along with privacy and security professionals, the Aug. 13 report, titled "Securing LLM Backed Systems: Essential Authorization Practices," describes LLM security risks associated with designing systems, outlines design patterns for extending LLM system capabilities and explores pitfalls in authorization and security.
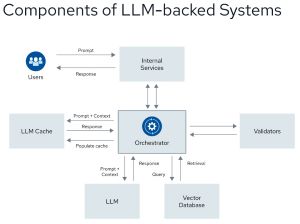 [Click on image for larger view.] Components of LLM Backed Systems (source: CSA).
[Click on image for larger view.] Components of LLM Backed Systems (source: CSA).
CSA said that while there has been rapid adoption of LLMs to tackle diverse business problems, guidance and best practices are scarce, especially when external data sources and using the LLM for decision-making processes are involved.
"System designers can use this guidance to build systems that utilize the powerful flexibility of AI while remaining secure," said CSA.
One easily digestible takeaway from the sprawling report is a list of fundamental principles and best practices — some tailored specifically to LLM systems — that CSA used for its recommendations:
- Output Reliability Evaluation: LLMs may produce unreliable results; their use should be carefully evaluated depending on the criticality of the business process involved.
- Authorization: The authorization policy decision and enforcement points should always reside outside the LLM to maintain security and control.
- Authentication: The LLM should never be responsible for performing authentication checks. The authentication mechanism used in the broader system should handle these checks.
- Vulnerabilities: Assume LLM-specific attacks like jailbreaking and prompt injection are always feasible.
- Access: Enforce least privilege and need-to-know access to minimize exposure and potential damage control lapses.
Those five items provide the basis for "best practices and considerations" and "pitfalls and anti-patterns" for a number of architecture design patterns for LLM-based systems, including:
- Retrieval-Augmented Generation (RAG) Access Using a Vector Database
- RAG via API Calls to External System
- LLM Systems Writing and Executing Code
- LLM-Backed Autonomous Agents
Autonomous Agents
The latter is one of the hottest areas in AI right now as it allows LLMs to go beyond simply responding to user prompts to actually take independent actions based on those prompts. While extremely useful, such authority comes with concerns and risks.
"Agent-based frameworks are still in their infancy, and many challenges and limitations remain when building agents," the report said. "Some of these challenges include having to adapt a role to effectively complete tasks in a domain, being able to do long-term planning, reliability or knowledge limitation. LLM agents also face the already mentioned challenge of non-determinism, which, while beneficial for generating creative ideas, poses risks in scenarios requiring high predictability."
Part of the best practices/considerations section of the autonomous agent section reads:
Knowledge bases should have access controls to prevent unauthorized access and ensure responses are generated based on permitted sources.
- External knowledge bases often have unique authorization controls, roles, enforcement, and other quirks. Abstracting all interactions with a given knowledge base into modules specific to that knowledge base compartmentalizes this complexity.
- Validate task planning with capabilities the orchestrator has knowledge of to prevent hallucinations of invalid steps.
Sandbox the orchestrator plugins as much as possible to adhere to the least privileged principles.
- Do plugins need full network access?
- What specific files do they need to interact with?
- Do they need read and write permissions, or is read access sufficient?
- For sensitive data, prompt the user for permission to perform said action
- If the system being interacted with only permits coarse-grained permissions, is it possible to integrate mitigating controls into the plugin?
A couple of agent pitfalls/anti-patterns include:
- Even within the trust boundary, agents should not fully trust other agents as each could be interacting with data from beyond the boundary.
- Consider reviewing and potentially enhancing the logging practices across the system, including external components. While it would be nearly impossible to log everything, implementing more comprehensive request tracing throughout the ecosystem that agents interact with could be valuable. Focus on key interactions and critical paths to improve visibility and troubleshooting capabilities without overwhelming the system or violating privacy concerns.
"Key principles emphasize the necessity of excluding LLMs from authorization decision-making and policy enforcement," concluded the report, prepared by CSA's AI Technology and Risk Working Group. "Continuous verification of identities and permissions, coupled with designing systems that limit the potential impact of issues, is crucial. Implementing a default-deny access strategy and minimizing system complexity are effective measures to reduce errors .... Additionally, rigorous validation of all inputs and outputs is essential to protect against malicious content."
The report also emphasized the importance of human oversight over any LLM. "Incorporating human in the loop oversight for critical access control decisions is recommended. This approach can enhance security, reduce the risk of automated errors, and ensure appropriate judgment in complex or high-stakes situations," the report said.