Ransomware Targeting Higher Ed Rose 70% in 2023, Malwarebytes Reports
- By Kristal Kuykendall
- 02/08/24
New research from Malwarebytes ThreatDown analysts shows that 2023 was the "worst year on record" for education, with a 105% jump in known ransomware attacks targeting the global education sector and a 70% rise in ransomware targeting higher education specifically — with nearly half targeting U.S. academic institutions.
According to an analysis of ransomware research by Marcelo Rivero at Malwarebytes, “known attacks” — those where the victim did not pay a ransom and the victims’ data was posted on the Dark Web — victimized education institutions 265 times in 2023, up from 129 the year before.
This provides the best overall picture of ransomware activity, but the true number of attacks is far higher, according to Malwarebytes’ blog summarizing the education-specific research.
Last year, 43% of ransomware education attacks affected higher education institutions, the firm said.
In its 2024 ThreatDown State of Malware report, Malwarebytes researchers review the most prominent cybercrime tactics and offers recommendations for addressing each emerging threat.
Five ransomware “gangs” were credited with 81% of 2023’s education ransomware attacks:
Key Findings: Trends in Education Ransomware
The ThreatDown report listed a number of trends, some new and some resurging in 2023:
So-called “Big Game Ransomware” rose last year, with ransom demands rising significantly, according to the report. “Since its emergence in 2018, big game’ ransomware has been the most serious cyberthreat to organizations all around the world,” the report said. “Big game attacks extort vast ransoms from organizations by holding their data hostage — either with encryption, the threat of damaging data leaks, or both.” The average ransom payment soared to about $750,000, and researchers estimate total ransom payments in 2023 could exceed $1 billion globally.
Ransomware groups are targeting a higher volume of targets at the same time. “For example, the CL0P ransomware gang broke established norms with a series of short, automated campaigns, hitting hundreds of unsuspecting targets simultaneously with attacks based on zero-day exploits,” the report said.
Malicious advertising — or malvertising — also made a comeback in 2023, researchers said, with widespread campaigns impersonating brands such as Amazon, Zoom, and WebEx to “deliver both Windows and Mac malware through highly convincing ads and websites that trick users into downloading malware on their devices.”
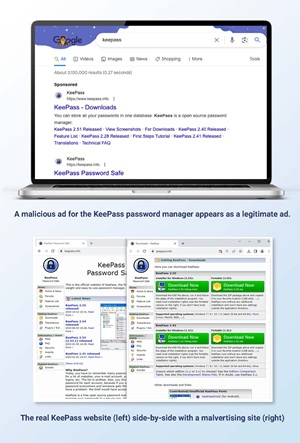
Malwarebytes ThreatDown Labs found that the five most-impersonated brands were Amazon, Rufus, Weebly, NotePad++ and Trading View; Dropbox, Discord, 4sync, Gitlab and Google emerged as the top five most-abused hosts.
The most frequently discovered malware: Aurora Stealer, Vidar, Redline Stealer, BatLoader, and IcedID.
Key Findings: OS-specific trends
-
Android banking trojans: Mawarebytes ThreatDown Labs detected Android banking trojans 88,500 times in 2023. In these attacks, Banking trojans are disguised as regular apps like QR code scanners, fitness trackers, or even copies of popular applications like Instagram to copy banking passwords and steal money directly from accounts.
-
Malware on Macs: Malware accounted for 11% of detections on Macs last year. Despite declining PC sales, demand for Macs has grown. Today Macs represent a 31% share of US desktop operating systems, while a quarter of businesses run Macs somewhere on their networks making Apple’s macOS an increasingly significant target for malicious actors.
-
Living Off the Land attacks: Abuse of Windows Management Instrumentation (WMI) was the top technique (27%) for Living Off the Land (LOTL) cyberattacks. In these attacks, criminals carry out malicious activities using legitimate IT administration tools like WMI or Powershell.
Read the full ThreatDown report at Malwarebytes.com.
About the Author
Kristal Kuykendall is editor, 1105 Media Education Group. She can
be reached at [email protected].