Cloud AI Services Slide Back to Rock Bottom in Gartner 'Hype Cycle'
Cloud AI services have moved from the "slope of enlightenment" to the "trough of disillusionment," according to Gartner's latest report on AI trends.
The research firm last month published "Hype Cycle for Artificial Intelligence, 2024," which shows cloud AI services have reached the bottom of the trough, which is the point in the cycle where interest in a technology wanes as early adopters fail to deliver on the technology's promises.
The stages are:
- The innovation trigger starts when an event, like a technological breakthrough or a product launch, gets people talking.
- The peak of inflated expectations is when product usage increases, but there's still more hype than proof that the innovation can deliver what you need.
- The trough of disillusionment happens when the original excitement wears off and early adopters report performance issues and low ROI.
- The slope of enlightenment occurs when early adopters see initial benefits and others start to understand how to adapt the innovation to their organizations.
- The plateau of productivity marks the point at which more users see real-world benefits and the innovation goes mainstream.
This year's report shows "Cloud AI Services" at trough bottom, several years after ChatGPT kicked off the generative AI paradigm shift.
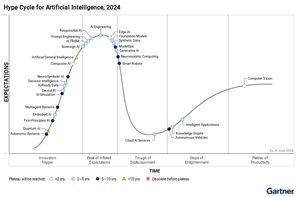 [Click on image for larger view.] Hype Cycle for Artificial Intelligence, 2024 (source: Gartner).
[Click on image for larger view.] Hype Cycle for Artificial Intelligence, 2024 (source: Gartner).
Last year, it was further up the axes for time and expectations, on the "slope of enlightenment."
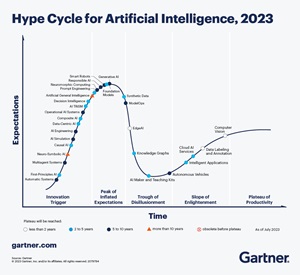 [Click on image for larger view.] Hype Cycle for Artificial Intelligence, 2023 (source: Gartner).
[Click on image for larger view.] Hype Cycle for Artificial Intelligence, 2023 (source: Gartner).
"Cloud AI services have regressed on the Hype Cycle since last year, due to the number of GenAI-based cloud AI services that have come to market," Gartner said in this year's report. "Vendors and end users of these services have experienced problems with service capacity, reliability, model update frequency and cost fluctuation, which may, however, be considered growing pains."
Generative AI, meanwhile, seems to be just edging up against the trough's border from the "peak of inflated expectations" part of the cycle, having been at the very pinnacle last year.
The two technologies are closely related, of course.
"Cloud AI services impact applications running the business allowing developers to enhance application functions," Gartner said. "Generative AI adds a new category to these solutions allowing for the fine-tuning of LLMs to tailor performance. Data-driven decisioning mandates inclusion of ML models to add application functionality. Some AI technologies are maturing, but generative AI includes less mature capabilities. Cloud AI services enhance applications with models that score, forecast and generate content enabling data-driven business operations."
Replacing Gen AI at the top this year are technologies like AI engineering, edge AI, responsible AI, prompt engineering, synthetic data and some others.
"On the Slope of Enlightenment are AI technologies that have many years of innovation behind them and are getting nearer to mainstream adoption," Gartner said. "Usage of autonomous vehicles has increased in some locations, despite severe skepticism in certain quarters, the imposition of restrictions and the withdrawal of some operating licenses. Intelligent applications, now powered by GenAI, have entered the workforce, but more time is needed to objectively quantify their impact on productivity."
The research firm's recommendations for organizations eyeing more involvement with cloud AI include:
- Choose customizable cloud AI services over bespoke models to address a range of use cases and for quicker deployment and scalability.
- Improve chances of success of your AI strategy by experimenting with AI techniques, including the use of generative AI models such as LLMs and multimodal models and other cloud services. Ensure that generative AI models are loosely coupled as the technology continues to evolve rapidly.
- Use cloud AI services to build less complex models, giving the benefit of more productive AI while freeing up your data science assets for higher-priority projects.
- Empower non-data-scientists with features such as automated algorithm selection, dataset preparation and feature engineering for project elements. Leverage existing expertise on operating cloud services to assist technical professional teams.
- Utilize pretrained generative AI models to allow for rapid prototyping and deployment of LLM-enabled solutions.
- Develop cost modeling tools that allow the enterprise to effectively predict both usage and management costs as AI models are broadly deployed in applications across the business.
The full report is available to Gartner clients here.