Faculty Expect to Return to Face-to-Face Instruction for Fall 2021, but with Online Elements
- By Dian Schaffhauser
- 12/15/20
A recent survey of faculty found that the reopening of campuses post-pandemic won't necessarily spell the end to online learning. Nearly half expect to embed the use of online elements into their instructional practices. While 51 percent of faculty said they'd return to in-person instruction, the rest said they'd employ some blend of online too — whether that be the hyflex model (14 percent); a blend of online synchronous and asynchronous with in-person (14 percent); online synchronous and asynchronous (10 percent); online asynchronous (8 percent); or online synchronous (3 percent).
The survey was done over the past five months by Top Hat, a company with an active learning courseware platform, among 1,500 college and university faculty, instructional support staff and administrators.
Last month, Campus Technology shared the results of a student survey done by the company. That survey found that three-quarters of students blamed a lack of engaging in-class experiences (77 percent) and a lack of face time with faculty and students (75 percent) for a "general sense of lethargy." The survey shared an additional data point: Where students agreed that their instructors have made an effort to understand their personal goals, interests and challenges, students were more likely to state that they expected to return to school in the spring — by 11 percentage points — 73 percent versus 62 percent for those who disagreed.
Among the tools that faculty said they were using in remote classrooms, learning management systems dominated (mentioned by 84 percent of respondents), followed by quizzing and testing tools (72 percent), lecture and video recording (71 percent), video streaming (69 percent) and homework tools (54 percent).
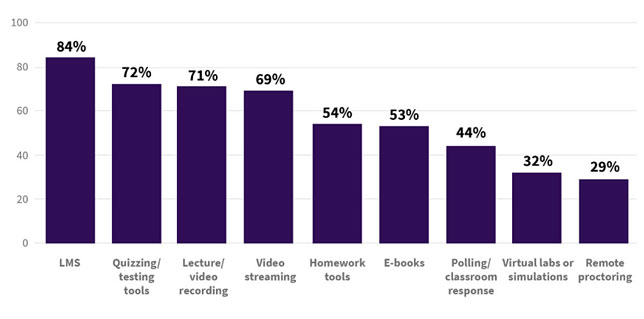
Tools used in remote classrooms
Yet, an increase in the number of tools used didn't translate to greater student engagement. While 65 percent of students said they lacked engaging in-class experiences in courses where a single tool was used, that jumped to 77 percent when instructors used four or more tools. Confusion also rose among students saying that they had difficulty using the online learning tools; that grew from 26 percent in single-tool classes to 42 percent in classes with four or more tools.
Additional survey findings are openly available on the Top Hat website.
About the Author
Dian Schaffhauser is a former senior contributing editor for 1105 Media's education publications THE Journal, Campus Technology and Spaces4Learning.