Report: Attackers Change Tactics as Ransomware Payoffs Decline
Attackers are changing tactics as they collect less money from ransomware payoffs, according to a new report from Chainalysis, a blockchain analytics firm.
For years, cybersecurity experts have advised that organizations not pay ransomware demands, and that practice seems to be gaining traction as the company noted a 35% year-over-year decrease in ransomware payments, with less than half of recorded incidents resulting in victim payments.
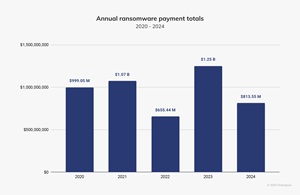 [Click on image for larger view.] Annual Ransomware Payment Totals (source: Chainalysis).
[Click on image for larger view.] Annual Ransomware Payment Totals (source: Chainalysis).
These payments have generally increased over the last five years — with 2022 an exception — and topped out at $1.25 billion last year according to the firm, which provides cryptocurrency investigation, compliance, and risk management solutions. Cryptocurrency is most often used for ransomware payments because of guaranteed pseudonymity, global accessibility, and difficulty in reversing transactions. These payments can still be tracked in certain ways, though, and the company's report provides exhaustive details about the entire ransomware ecosystem.
"The ransomware landscape experienced significant changes in 2024, with cryptocurrency continuing to play a central role in extortion," the report said. "However, the total volume of ransom payments decreased year-over-year (YoY) by approximately 35%, driven by increased law enforcement actions, improved international collaboration, and a growing refusal by victims to pay."
With that reduction in payments however, the threat actors are changing their approaches in the eternal back-and-forth struggle between the black-hatters and white-hatters.
"In response, many attackers shifted tactics, with new ransomware strains emerging from rebranded, leaked, or purchased code, reflecting a more adaptive and agile threat environment," Chainalysis said. "Ransomware operations have also become faster, with negotiations often beginning within hours of data exfiltration. Attackers range from nation-state actors to ransomware-as-a-service (RaaS) operations, lone operators, and data theft extortion groups, such as those who extorted and stole data from Snowflake, a cloud service provider."
Overall, crypto crime is paying off to the tune of a predicted $51.3 billion in 2024, according to a Chainalysis report published last month.
"According to our metrics today, it looks like 2024 saw a drop in value received by illicit cryptocurrency addresses to a total of $40.9 billion," that Jan. 15 report said. "However, 2024 was likely a record year for inflows to illicit actors as these figures are lower-bound estimates based on inflows to the illicit addresses we've identified up to today."
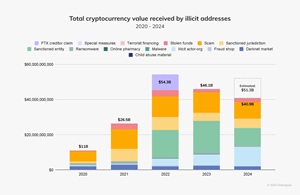 [Click on image for larger view.] Total Cryptocurrency Value Received by Illicit Addresses (source: Chainalysis).
[Click on image for larger view.] Total Cryptocurrency Value Received by Illicit Addresses (source: Chainalysis).
That overall crypto crime report also addressed the ransomware scene specifically — apparently based on the same data — indicating ransomware remains a lucrative crime. While it still generates hundreds of millions in revenue, major law enforcement crackdowns and a growing reluctance among victims to pay have disrupted the ecosystem. Despite these challenges, attack volume remained steady in 2024, with some groups still securing payments, though in smaller amounts. In fact, a report from Cohesity in January 2024 concluded that ransomware payoffs were becoming a "cost of doing business."
Chainalysis provided this summary of navigating the evolving threat landscape:
"Ransomware in 2024 reflected shifts driven by law enforcement action, improved victim resilience, and emerging attack trends. Crackdowns and collaboration with incident response firms and blockchain experts helped disrupt many ransomware groups, reducing their profitability. Victims also demonstrated greater resistance to ransom demands, widening the gap between demands and payments.
"Financial strategies continue to adapt under law enforcement pressure, although malicious actors face increasing difficulties laundering payments from victims. Sustained collaboration and innovative defenses will remain critical to building on the progress made in 2024."
The full report is available on the Chainalysis site.
About the Author
David Ramel is an editor and writer at Converge 360.