Electronic Textbooks
E-books are being widely adopted as alternatives to traditional textbooks. Here you'll find articles detailing new developments in the area of e-book and e-textbook technologies, along with stories about institutions adopting them.

Knewton has updated its subscription options to allow students to access multiple courses. Priced at $79.99, the new Altapass gives students unlimited use of multiple Alta products across a single subject area for up to two years.

Learning materials publisher FlatWorld is now offering Flatworld Institutional, a textbook subscription service that allows universities and departments to tailor the textbook selection to students' specific needs.
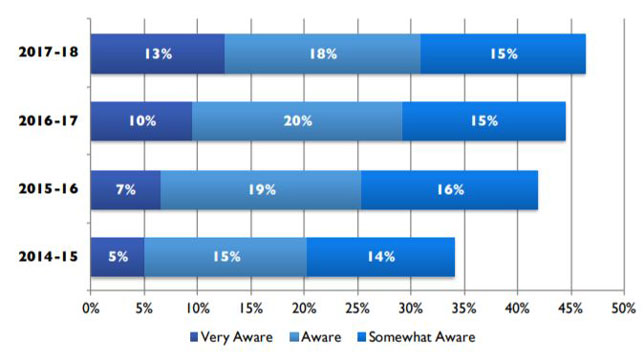
The use of open educational resources could be at a turning point: It's beginning to shake off its fringe reputation and gain greater recognition among faculty and department heads. A recent Babson Survey Research Group study found "steady growth in awareness" among these individuals and predicted that adoption growth could accelerate.

For the second year running, library collections in higher education now contain more digital items than physical. According to preliminary numbers issued by the Education Department's National Center for Education Statistics, of the 2.5 billion items in colleges and universities in 2017, 59 percent were digital — books, databases, media and serials — and 41 percent were physical.

In our 2018 Teaching with Technology Survey, faculty members told us about their most-wanted hardware and software, feelings on tech's value for learning, technologies they're using in class and more.
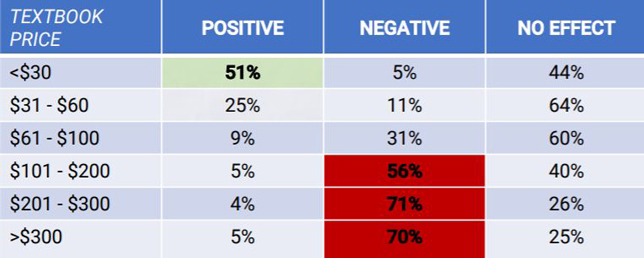
According to a recent survey, faculty members who choose course materials that cost less than $30 are 10 times more likely to get a positive rating from students than a negative rating. The survey was undertaken by textbook publisher FlatWorld.

Several of McGraw-Hill Education's digital course materials will now feature embedded audio- and video-capture capabilities from video platform GoReact.
A $4.9 million grant will enable the University of California, Davis and a consortium of other institutions to build out a set of open textbooks intended for chemistry and career and technical education courses. The U.S. Department of Education Office of Postsecondary Education awarded the four-year grant as part of an open textbooks pilot program, which was funded by Congress as part of the 2018 omnibus spending bill.
Ivy Tech Community College in Indiana recently announced it will use BioBeyond as the standard course for all of its online introductory biology courses. The college, which has more than 40 campus locations serving nearly 71,000 students, piloted the digital biology course over the summer, and now plans to use it in 37 online sections.

Ed tech company Perceivant is introducing 15 new "courses" — interactive courseware designed to replace the traditional textbook.